Cybersecurity Checklist for Your Business: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Assets
In today’s digital world, where nearly every business relies on technology to some degree, cybersecurity has become a crucial pillar for success. Unfortunately, it’s also one of the most overlooked aspects of running a business. Many small and medium-sized companies believe they are not significant enough to attract cybercriminals. However, this assumption couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, smaller businesses are often the primary targets because they tend to have weaker security measures compared to larger corporations.
Cyberattacks can have devastating consequences, from financial loss to irreversible damage to a company’s reputation. The average cost of a data breach in the United States has surpassed $4 million, a number that can cripple many businesses. Beyond monetary losses, cyberattacks can erode customer trust, disrupt operations, and expose sensitive information to malicious actors. With threats like ransomware, phishing, and data breaches on the rise, safeguarding your business from digital threats is more important than ever.
The good news is that protecting your business doesn’t require an army of IT experts or an enormous budget. It starts with implementing a systematic approach to cybersecurity. Below, we present a detailed checklist designed to help you identify vulnerabilities, strengthen defenses, and ensure your business is prepared to face modern threats.
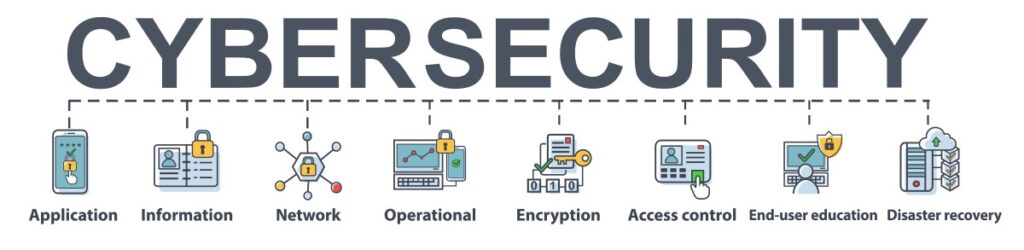
Step 1: Assess Your Current Cybersecurity Posture
The first step in creating a strong cybersecurity strategy is understanding where your business currently stands. Start by conducting a comprehensive audit of your technology infrastructure. This means taking inventory of all hardware, software, and digital assets used in your operations. Include everything from employee laptops to third-party software tools, as well as customer databases and cloud storage accounts.
Once you have a clear picture of your assets, evaluate your existing security measures. Are your systems up to date? Do you have firewalls and antivirus software installed? How well are you protecting sensitive customer data? Performing a risk assessment can help you identify potential vulnerabilities. For instance, if your team is frequently working remotely, do they use secure networks to access company systems? By pinpointing these gaps, you can create a tailored action plan.
Step 2: Strengthen Passwords and Authentication
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to boost your cybersecurity is by enforcing strong password policies. Weak passwords remain a leading cause of data breaches, giving cybercriminals easy access to sensitive systems. Require all employees to use passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Passwords should never be reused across accounts.
Taking this a step further, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for critical systems. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a secondary method, such as a one-time code sent to their smartphone. It’s an additional step that makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access, even if they have a password.
To simplify password management, encourage the use of reputable password managers. These tools can securely store and generate complex passwords, reducing the likelihood of human error.
Step 3: Protect Your Network Infrastructure
Your network serves as the backbone of your business operations, and securing it should be a top priority. Start by ensuring that a robust firewall is in place to monitor and control traffic entering and exiting your network. Firewalls act as a first line of defense, filtering out potentially harmful traffic before it reaches your systems.
For businesses with remote teams, virtual private networks (VPNs) are essential. A VPN encrypts data transmitted between devices and your network, protecting it from interception by malicious actors. This is particularly important if employees are using public Wi-Fi networks, which are notoriously insecure.
Additionally, keep your network hardware, such as routers and switches, up to date with the latest firmware. Outdated firmware often contains vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Regular updates ensure that your equipment is equipped with the latest security patches.
Step 4: Regularly Update and Patch Your Software
Outdated software is one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks. Every software product—whether it’s an operating system, a customer relationship management (CRM) tool, or an email platform—has vulnerabilities that are periodically discovered and patched by developers. If you’re not staying on top of these updates, you’re leaving your business exposed.
To mitigate this risk, enable automatic updates for all software and operating systems used in your business. For applications that don’t support automatic updates, establish a schedule to manually check for and install updates. This process should also include reviewing third-party tools and plugins, as these are often overlooked despite being potential security risks.
Step 5: Train Your Employees to Recognize Cyber Threats
Even the most advanced cybersecurity tools can be rendered useless if employees are not educated about potential threats. Human error is a leading cause of data breaches, often stemming from phishing attacks or accidental disclosures. By training your team, you can turn them into your first line of defense.
Conduct regular workshops to teach employees how to identify phishing emails, which often disguise themselves as legitimate messages to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. Suspicious signs, like grammatical errors or urgent requests for personal details, should raise red flags.
Additionally, establish a clear protocol for reporting potential security incidents. Employees should feel confident that they can alert IT staff without facing repercussions, even if they suspect they’ve clicked on a malicious link. Providing ongoing education about emerging threats ensures that your team remains vigilant.
Step 6: Implement Endpoint Security for All Devices
In today’s mobile workforce, employees often use personal devices to access company systems. While convenient, this trend also increases your attack surface. Implement endpoint security measures to protect devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
Install antivirus and anti-malware software on all company devices. For mobile devices, consider implementing mobile device management (MDM) solutions, which allow you to enforce security policies remotely. This includes the ability to wipe data from lost or stolen devices.
Regularly scan all devices for potential threats, and remind employees to keep their personal devices updated with the latest security patches.
Step 7: Back Up Your Data Regularly
Data backups are a critical safety net that can save your business in the event of a ransomware attack, hardware failure, or natural disaster. Develop a comprehensive backup strategy that includes both local and cloud-based storage solutions.
Automate the backup process to ensure it happens consistently, and store copies of your backups in secure offsite locations. It’s equally important to test your backups periodically to confirm that data can be restored quickly and without issues.
With a solid backup system in place, your business can recover from catastrophic events with minimal downtime and data loss.
Step 8: Limit Access to Sensitive Data
Not every employee needs access to all areas of your network or systems. By limiting access to sensitive data, you reduce the risk of accidental breaches and insider threats. Adopt a role-based access control system, which assigns permissions based on an employee’s specific responsibilities.
For example, a marketing employee likely doesn’t need access to financial records, while an HR representative might require limited access to payroll systems. Adhering to the principle of least privilege ensures that employees only have the access they need to perform their jobs.
Monitor access logs regularly to detect any unauthorized attempts to access restricted data. If an employee leaves the company, immediately revoke their access to all systems.
Step 9: Develop and Test an Incident Response Plan
No matter how strong your defenses are, cyberattacks can still occur. The key to minimizing damage is having a well-defined incident response plan. This plan should outline the steps your team will take in the event of a cybersecurity breach, including who will be responsible for specific actions.
The plan should include guidelines for containing the attack, communicating with affected parties, and restoring compromised systems. After an incident, conduct a thorough review to determine what went wrong and how you can improve your defenses moving forward.
Regularly test your incident response plan with simulated drills to ensure that everyone knows their role and can act quickly in a real emergency.
Cybersecurity is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process that requires constant attention and adaptation. As cyber threats evolve, so must your defenses. By implementing the steps outlined in this checklist, your business can significantly reduce its risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
Investing in cybersecurity is not just about protecting data—it’s about protecting your business, your customers, and your reputation. In an era where trust is everything, showing your commitment to security can even become a competitive advantage. Take the time to assess your vulnerabilities, educate your team, and establish strong protocols. The peace of mind you’ll gain is well worth the effort.
